Retaining rings – circlips
These are metal fasteners that secure pins and shafts against axial displacement, machine parts in holes or shafts. This eliminates threading, drilling or other machining associated with traditional fasteners such as bolts, nuts, pruners, etc.
Advantages of retaining rings
» Less modification of shaft or bushing (drilling, threading, etc.)
» Smaller size and weight
» Lower cost of raw materials and labor
Seeger outer and inner rings
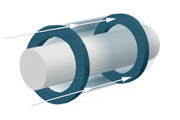
These rings are installed horizontally along the axis. This includes the retaining rings on the shaft and the hole. The Seeger retaining rings on the shaft and the hole have a tapered cross-section towards the ends. This shape allows for high ring elasticity and proper seating in the groove. Seeger's safety rings are provided with meshes at the ends, which, with the help of seeger pliers, fit into the groove on the shaft or in the case.

Outer Seeger's safety rings
The outer seeger safety rings are manufactured to DIN 471. They are used to secure the shaft. The dimensions of the seeger´s safery rings are given by the diameter of the shaft, but the size of the ring can not be precisely determined by its measurement. Installation of the Seeger's safety ring is carried out with the help of the seeger pliers, which seeger grip on the mounting eyes, stretches and slides into the groove on the shaft. After loosening, the seeger´s safery rings pulls out and firmly anchors.

Inner Seeger's safety rings
The internal seeger safety rings are manufactured to DIN 472. They are used to secure the case. Also, the internal dimensions can not be determined by measuring it. Installation is by pressing the ring using the mesh and seeger pliers and inserting it into the case. After inserting into the groove and releasing the pliers, the seeger safety rings extends to the original shape again to secure the case.
Segerovy pojistné kroužky – konstantní průřez


Retaining rings with a constant cross-section are a cheaper option compared to classic seegers with a tapered cross-section, but they only provide three-point locking of the shaft or bushing, see picture. The advantages of these retaining rings include the absence of mounting lugs, allowing space-saving radial savings. It is not even necessary to use special mounting tools.

Bearing Retaining Rings
Retaining rings with constant cross-section also include bearing retaining rings manufactured to DIN 5417. They are used to secure bearings on the shaft.

Wire Retaining Rings
Wire circlips are made to DIN 7993. Like other circlips, these are also used to secure the shaft or sleeve. After installation in the groove, the assembly holds the part of the ring in place, which protrudes.
E-clips


Clamp safety rings are especially used for small shafts and are designed for applications with low axial loads. The E-clip is manufactured in accordance with DIN 6799. Compared to the outer and inner segmented lock, the E-clip is not equipped with meshes and is deposited in a radial position (vertically to the axis). Thanks to its shape, the fuse snaps into the groove correctly and thus fulfills its function.
Self-locking retaining rings
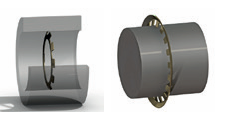
These are sealing rings for shafts and housings. These safety rings do not require a groove for their seating. These are small size rings for applications with very low axial loads. Most of these locking rings are relatively difficult to remove after installation.
Spiral safety rings

These are spirally wound safety rings used for both shafts and grooves. Made either simple - single thread or multiple, depending on application requirements. Due to the absence of mounting meshes, the spiral rings offer space saving in the radial direction.

These spiral wound rings can also be provided with waves. This option enables the shaft or housing to be secured, as well as compensation for the axial clearance (influence of thermal expansion, tolerances, etc.). The advantages of this seal also include the precise setting of the load by determining the thickness of the wire, the number of waves and threads.
Wavy safety rings

These are machine parts that allow for elastic deformation - they deform with force, but when it stops acting, it returns to its original shape. They are used to cushion the machine part so that the shocks and vibrations of the unsprung parts are not transmitted to the sprung part.
Wavy safety rings are made of flat wire with the addition of waves for spring effect. An advantage over conventional springs is the use of a smaller working space with the same force. This means that the material is saved and, therefore, lower production costs.

Advantages of a wavy safety ring:
» Saves the space in the axial direction by up to 50% of the operating height
» Wave bending guarantees 100% axial load transfer
» Save space in radial direction against disc springs
» Unlimited range of forces allows combinations of factors: wire thickness, material, number of waves, number of turns,etc.
Wire rings can be simple (single thread only) or multiple. The stiffness of the wavy lock ring is directly proportional to the number of turns. For simple locking rings, the possibility of delivery is either with a gap or overlap. Multiple safety rings can also be delivered with a straight edge.